

The fact that the integrity of the cortex has been overcome results in fracture of the convex surface.
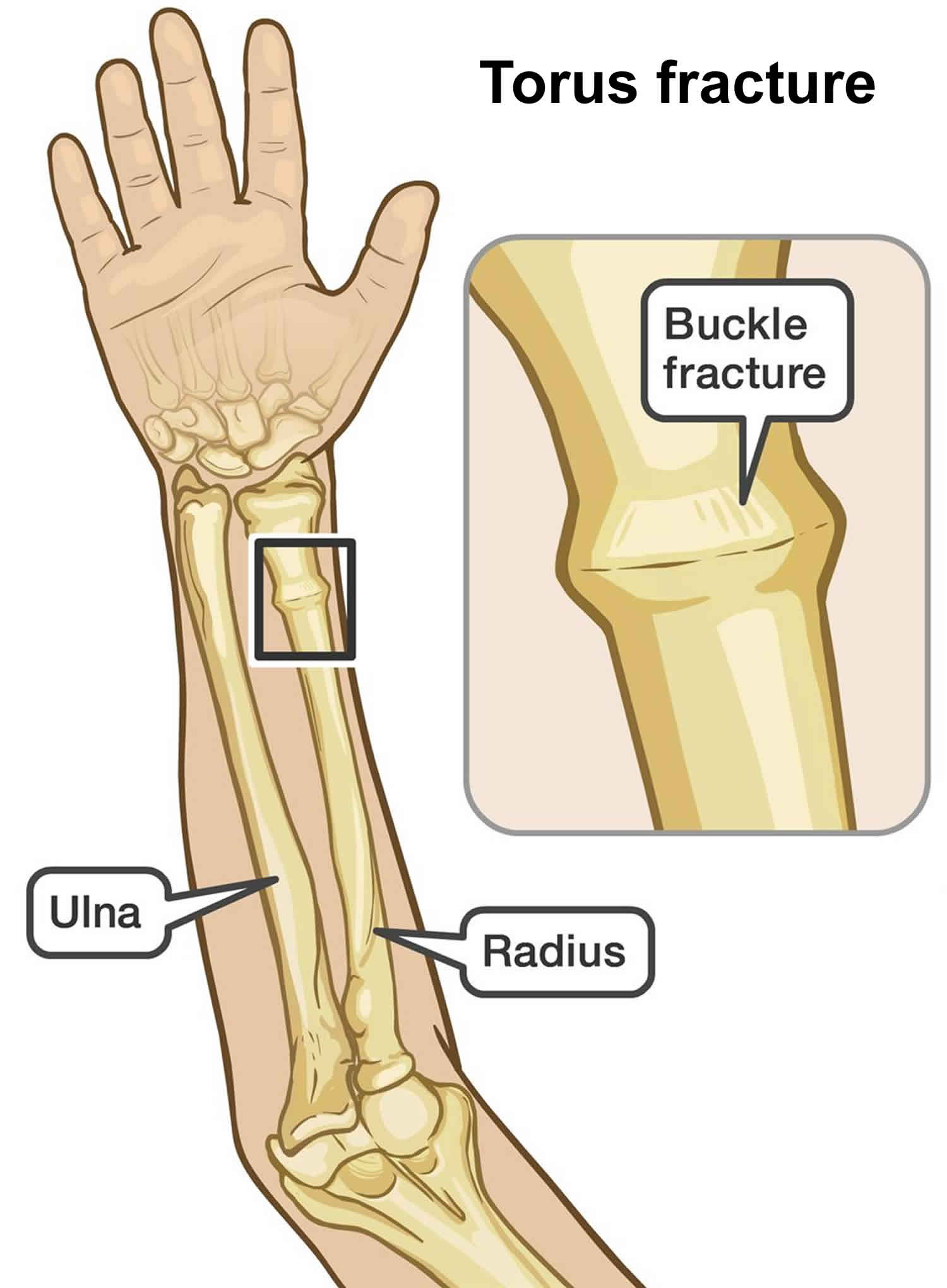
Buckle fractures of the distal radius in children. Greenstick fractures occur when the force applied to a bone results in bending of the bone such that the structural integrity of the convex surface is overcome. Fractures in children.īen-yakov M, Boutis K.
BUCKLE FRACTURE RADIUS SERIES
Short arm cast: Casting immobilization series for primary care. Garcia-rodriguez JA, Longino PD, Johnston I. Outcomes of long-arm casting versus double-sugar-tong splinting of acute pediatric distal forearm fractures. Levy J, Ernat J, Song D, Cook JB, Judd D, Shaha S. Buckling down on torus fractures: has evolving evidence affected practice?. Williams BA, Alvarado CA, Montoya-williams DC, Matthias RC, Blakemore LC. Epidemiology of Pediatric Fractures Presenting to Emergency Departments in the United States. Buckle fracture Pediatric Distal Radius Fractures Other Distal Radius Fractures Distal radius and or ulna metaphyseal Fractures - Distal forearm or wrist. Naranje SM, Erali RA, Warner WC Jr, Sawyer JR, Kelly DM. Greenstick Fractures.Īmerican Academy of Pediatrics. This includes physical injuries, medical bills, and pain and suffering.National Library of Medicine StatPearls. You may be eligible to recover for your child’s damages. If someone else’s negligence caused your child’s injury, such as a defective piece of playground equipment or a reckless sports coach, speak to an attorney. Common Causes of Torus Fractures in ChildrenĪ torus fracture can be very painful for a child, and result in expensive medical bills for treatment and casting. In some cases, a doctor might recommend a cast instead of a removable splint.
BUCKLE FRACTURE RADIUS MANUAL
Torus fractures generally do not require surgery, although manual manipulation may be necessary in the presence of severe angulation. During certain activities for the next two weeks, such as sports or playing on the playground, a child may put the splint back on to reduce the risk of further injury. A doctor may prescribe ibuprofen for pain control.Īfter just two to four weeks of immobilization, a torus fracture should heal enough to discontinue immobilization and begin rehabilitation exercises. A splint lets a child return to normal functioning faster than a cast. Once diagnosed, the most common treatment for a torus fracture is a removable splint. The appearance of a torus fracture can be subtle. In some cases, diagnosis stems only from the presence of angulation in the forearm. The buckle of the cortex or a subtle deformity may be apparent with a plain radiograph, but it will not show fracture lines. During the examination, a doctor should also test to see whether the fracture has affected the nerves and blood circulation in the arm.Ī doctor will order scans and tests to diagnose a torus fracture. An inability to rotate the forearm may also signal a buckle fracture. The doctor will look for severe pain, tenderness, swelling, and deformity of the elbow, forearm, or wrist. When a child exhibits symptoms of a torus fracture, the doctor will perform a physical examination of the forearm or other affected area. Diagnosing and Treating Torus Fractures in Children Numbness is a sign of a potential nerve injury. A child with a torus fracture may feel severe pain, as well as numbness in the forearm and hand. Torus fractures of the distal radius, or the shorter of the two arm bones, are the most common in children. These bones can buckle and break in a child after a fall directly onto the forearm, onto an outstretched arm, or from a direct blow to the forearm. The ulna and the radius are the forearm’s two main bones. Our outcomes focused on 5 aspects of patient care: immobilisation method and duration, clinical follow-up, radiological follow-up and the use of diagnostic ultrasound. They are most common in children under the age of 10, due to greater bone elasticity.įall fractures commonly occur as an ulna or radius fracture in the forearm. All prospective, retrospective or randomised trials involving the management of distal radius torus fractures in patients aged 018 years were included. This is a good thing, as it reduces the odds of needing surgery to put the bones back in place prior to casting or splinting. Torus fractures are stable fractures, meaning the broken pieces of bone are not displaced, or separated out of position. Torus fractures are also called buckle fractures because they occur when the topmost layer of a bone becomes compressed, causing the other side to bend away (or buckle) from the growth plate. A child’s bones heal more quickly than an adult’s, making it important to seek treatment as soon as possible to prevent future problems. A child may suffer a torus fracture when he or she falls and lands on an outstretched arm. Because of this, they occur more commonly in the forearm and wrist than the legs. Falls are the most common cause of torus fractures, in sports accidents or while playing on the playground. Posted in Injury Information on May 23, 2017Ī torus, or buckle, fracture can occur in children when something applies compressive force to an immature bone.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
